The landscape of HR outsourcing includes different models that businesses can leverage to optimize their workforce management. HCM (Human Capital Management), PEO (Professional Employer Organizations), and ASO (Administrative Services Organizations) are three popular approaches, and they differ in the level of involvement and the services they offer.
Since 1999, www.StaffMarket.com has helped over 20,000 companies evaluate the complex landscape of HR Outsourcing models through our leading network and team of independent industry experts in the USA.
Here’s a breakdown of the differences between a few of the most common Human Resources Outsourcing (HRO) Models:
1. HCM (Human Capital Management)
Overview: HCM is a broad term that refers to the strategic management of an organization’s workforce, which encompasses everything from recruitment and onboarding to performance management, training, and development. When you hear about HCM solutions, they typically refer to software or platforms that help businesses manage their workforce more effectively.
Key Features:
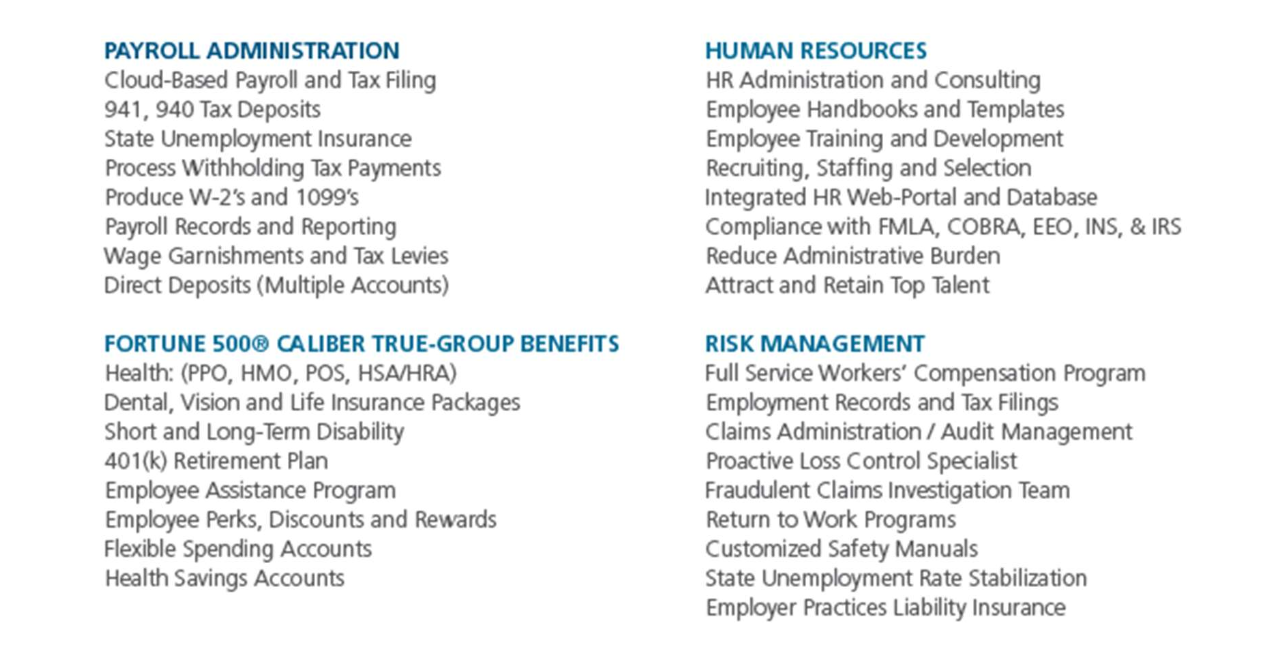
- Comprehensive HR Suite: HCM software typically includes tools for recruiting, payroll, performance tracking, time and attendance, learning and development, and analytics.
- Automation: Automates administrative tasks like payroll, benefits administration, and compliance reporting.
- Employee Self-Service: Offers employees access to view and manage their personal data, time off, and benefits.
- Data-Driven Decisions: Leverages analytics to track and optimize talent management, employee performance, and workforce productivity.
Who uses HCM?
- Larger businesses (companies with hundreds or thousands of employees).
- Organizations looking to enhance HR functions and make data-driven decisions using integrated software solutions.
2. PEO (Professional Employer Organization)
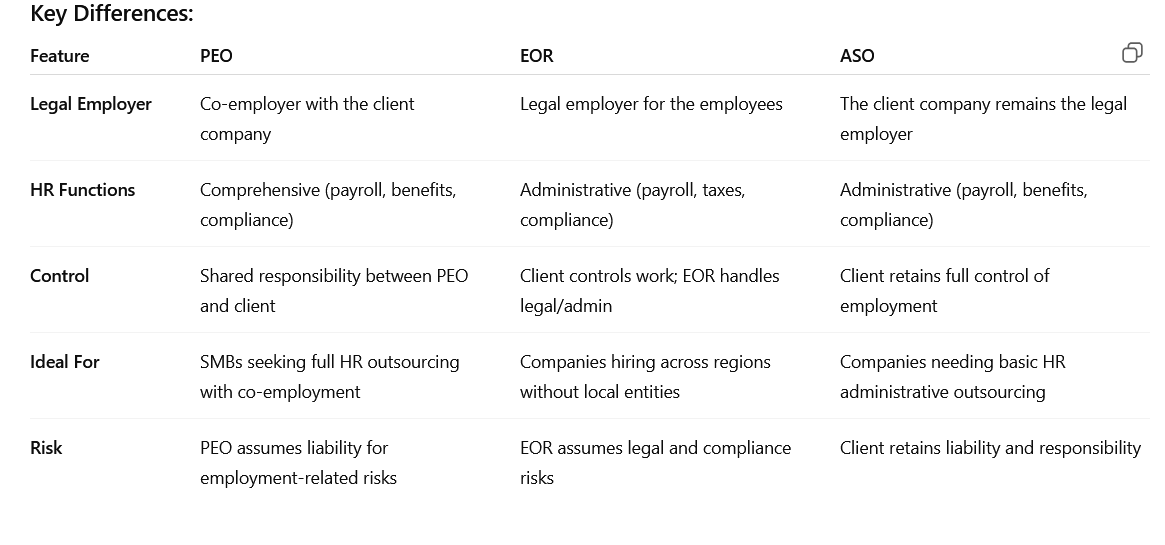
Overview: A PEO is a comprehensive outsourcing solution in which the PEO becomes a co-employer alongside your company. It handles many of the HR functions while you retain control over the day-to-day operations. A PEO assumes responsibility for areas like payroll, taxes, benefits administration, compliance, and risk management.
Key Features:
- Co-Employment: The PEO becomes a co-employer of your workforce, which means they share responsibilities for things like payroll, taxes, and compliance. Your employees are on the PEO’s books for administrative purposes, but you still manage their roles and responsibilities.
- Employee Benefits: A PEO can offer better benefits packages by pooling employees from different companies, which allows smaller businesses to access the same high-quality benefits (health insurance, 401(k), etc.) that large companies offer.
- Risk Management: PEOs handle workers’ compensation, unemployment insurance, and other risk-related issues, ensuring compliance with laws and regulations.
- Compliance: They help ensure your company remains compliant with federal, state, and local regulations, reducing the risk of legal issues.
Who uses PEO?
- Small to mid-sized businesses (typically under 1,000 employees) that need help managing HR but still want to retain control over day-to-day operations and culture.
PEO vs. HCM:
- PEOs take a higher level of control over HR functions (e.g., payroll, benefits), whereas HCM is software that helps you manage HR tasks yourself.
- With a PEO, your company shares responsibility for employees (co-employment), but with HCM, you remain the sole employer
- PEOs are ideal for businesses that want to outsource the bulk of HR functions to experts while maintaining operational control and receive a level of risk and liability mitigation through the PEO
3. ASO (Administrative Services Organization)
Overview: An ASO is an outsourcing model where the provider handles administrative HR functions, but the company retains the responsibility for employment-related decisions (like hiring, firing, and employee management). Unlike a PEO, the company does not enter into a co-employment arrangement with the ASO. The ASO typically handles administrative tasks such as payroll, benefits administration, and compliance.
Key Features:
- Administrative Support: ASOs focus on providing administrative HR services, such as payroll processing, benefits management, and compliance assistance. They don’t provide the co-employment relationship that a PEO does.
- Flexibility: Since the company remains the sole employer, they have more control over HR decisions and employee relations.
- Risk Management: The ASO helps manage risks related to HR tasks (like ensuring compliance with labor laws) but doesn’t take on the responsibility for workers’ compensation or other areas covered by a PEO.
ASO vs. PEO vs. HCM:
- The main difference between an ASO and a PEO is that the ASO doesn’t have the co-employment relationship, so the company retains complete control over its employees.
- HCM software is typically used in-house, while an ASO is an external service provider that handles administrative tasks.
Which Model of HR Structure is Right for You?
- HCM: If you’re looking for a technology-driven solution to automate HR tasks and gain insights into workforce performance but still want to manage things internally.
- PEO: If you want to outsource most HR functions (including compliance, payroll, benefits) and access better employee benefits while sharing employment responsibility with a partner and receiving risk mitigation
- ASO: If you want to retain control over your employees and HR decisions but need support with administrative tasks like payroll, benefits, and compliance and do not want to enter the co-employer relationship
In many cases, a unique combination of two of these (Ex. In house HR management + Outsourcing Providers) are the best approaches for a high performing business with solid growth trajectory. Specifically in businesses that are growing with locations in multiple states that face different employment laws, regulation, and compliance in each additional state they operate.
For example, using a PEO in combination with an in-house HR manager who oversees the outsourced solution (including added risk/liability mitigation) instead of hiring multiple in-house HR managers (who require a significant salary and do not provide any additional risk mitigation for you as the business owner).
Employer of Record (EOR): For companies hiring employees in foreign countries, or those who don’t want to set up a local legal entity in a new state or region, an EOR has a distinct value proposition in the appropriate setting and needs-based situation.
However, with thousands of providers out there it may be difficult to decide which combination and which provider is the most suitable for you businesses unique needs…
Still Have Questions? We have answers.
The good news…you are not alone! Since 1999, StaffMarket has helped over 20,000 companies evaluate the complex landscape of HR Outsourcing models through our leading nationwide network and team of independent expert consultants. We serve a large variety of industries including high-risk and hard to place accounts with workers compensation claims difficulty.
At www.staffmarket.com we specialize in getting the best rates available for group health insurance and workers compensation for our clients through our nationwide marketplace where top providers engage in a competitive bidding process to get you the best solutions, at the best rate, the first time. We exist to serve the strategic long-term growth of your company.
Our services are 100% free to use for our clients. No credit cards, no subscriptions, no BS. Get started today at: https://www.staffmarket.com/register or call us directly at 877-882-7225
Author: Brice Hamilton, Director of Business Development
Contact: brice@staffmarket.com